Welcome back to FilmmakingElements.com, this is Salik, the author of the blog. In this article, we will delve into the world of Optical Flow in DaVinci Resolve, a method used for Frame Interpolation. With over 10 years of experience in filmmaking and as a certified DaVinci Resolve Trainer, I have utilized DaVinci Resolve for numerous projects, harnessing the power of Optical Flow to enhance the visual fluidity of my works.
Understanding Optical Flow for Frame Interpolation: A Primer
Frame Interpolation is a fundamental technique for achieving seamless slow-motion effects or managing footage with varying frame rates, particularly in professional video editing platforms like DaVinci Resolve. Alongside Frame Blending, Optical Flow is another subset of Frame Interpolation that is instrumental in achieving smooth transitions between frames to craft visually appealing motion.
What is Optical Flow?
Optical Flow is a sophisticated technique utilized to generate new intermediary frames between existing ones by analyzing the motion trajectory and speed of objects within consecutive frames. Unlike Frame Blending, which primarily averages or blends pixel values, Optical Flow takes into consideration the motion vectors and the spatial-temporal characteristics of the footage to create more accurate and visually coherent intermediary frames.
This process is crucial when aiming to slow down your footage or deal with footage of differing frame rates, providing a smoother, more natural motion while avoiding the usual jitter or choppiness associated with standard frame rate conversions.
Significance of Optical Flow in Frame Interpolation:
Frame Interpolation encompasses techniques like Frame Blending and Optical Flow to produce new frames in a sequence, thus refining the motion in videos. While Frame Blending is simpler and faster, Optical Flow provides a more refined and accurate result by understanding the movement trends between frames to generate new intermediary frames. Grasping the intricacies of Optical Flow is pivotal to mastering Frame Interpolation in DaVinci Resolve, enabling you to choose the most suitable method based on your project needs.
Optical Flow, with its advanced motion analysis, tends to be the preferred choice for professional videographers and editors looking to achieve high-quality slow-motion effects and seamless frame rate conversions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Optical Flow in DaVinci Resolve on the Edit Page
Optical Flow is an essential technique within the realm of Frame Interpolation, especially when you’re working with slowed-down footage and aim to achieve smoother, more fluid motion. DaVinci Resolve provides an intuitive platform for executing Optical Flow, ensuring that your visuals are not only captivating but also professionally polished. In this section, we’ll meticulously guide you through the process of applying Optical Flow on a clip level within the Edit page of DaVinci Resolve.
Preparing Your Workspace
Before delving into it, ensure you have your project opened in DaVinci Resolve, with the clip you intend to work on already imported and placed on the timeline.
Navigating to the Edit Page
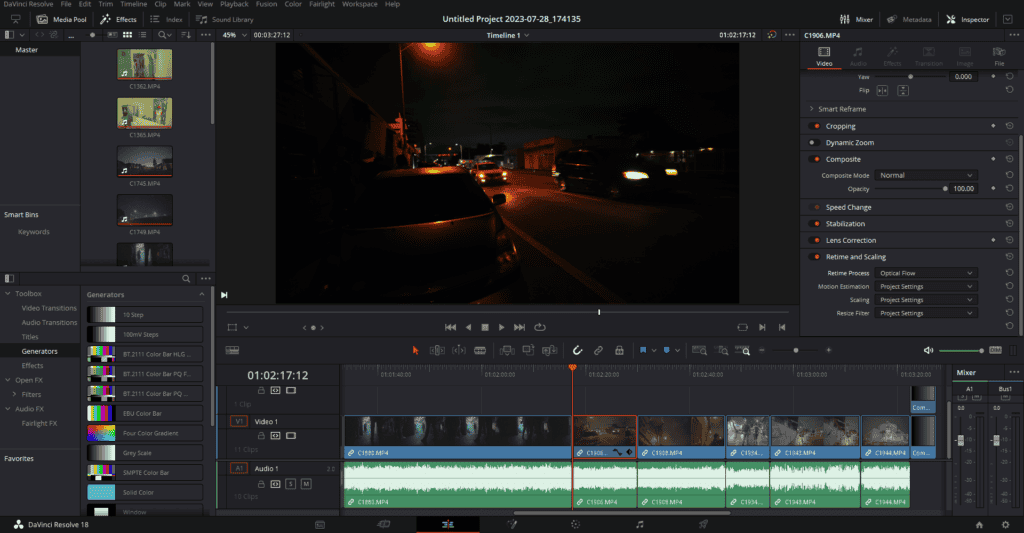
- Accessing the Edit Page: Begin by navigating to the Edit page of DaVinci Resolve. This can be done by clicking on the ‘Edit’ tab located at the bottom of the screen.
Selecting Your Clip
- Choosing the Desired Clip: Click on the clip on your timeline that you’ve slowed down or wish to apply Frame Interpolation to. It’s crucial to select the right clip to ensure the desired outcome.
Accessing Inspector Panel
- Opening the Inspector Panel: Once your clip is selected, proceed to click on the ‘Inspector’ button, which is situated in the top right corner of the interface. The Inspector panel is where you’ll find the settings necessary for it.
Navigating to Retime and Scaling Settings
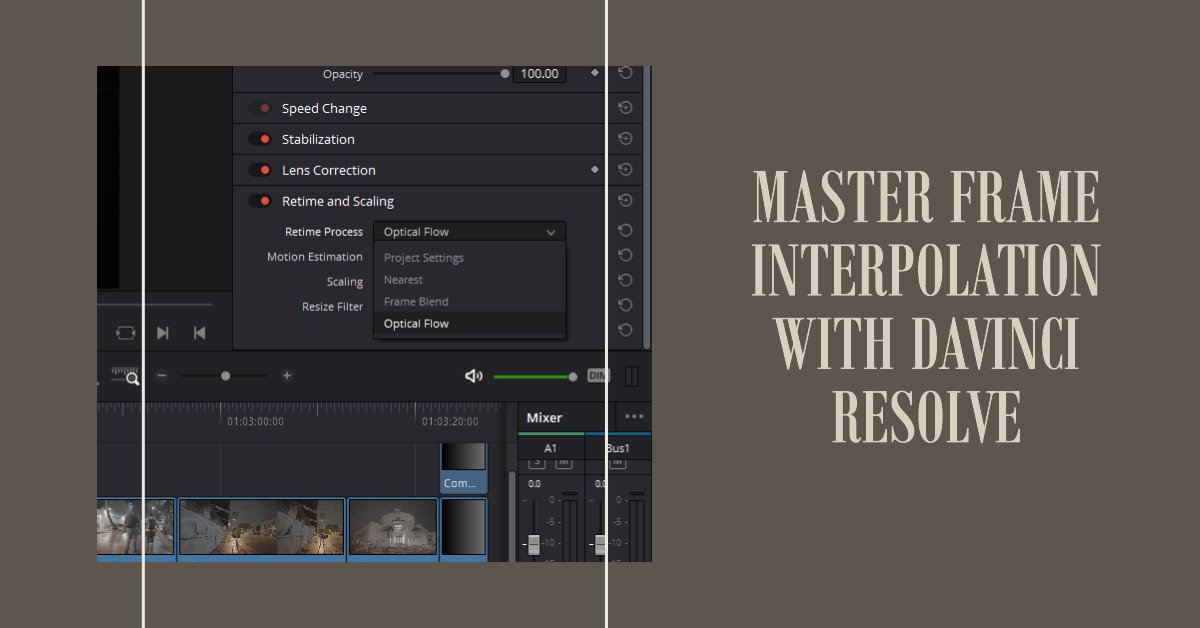
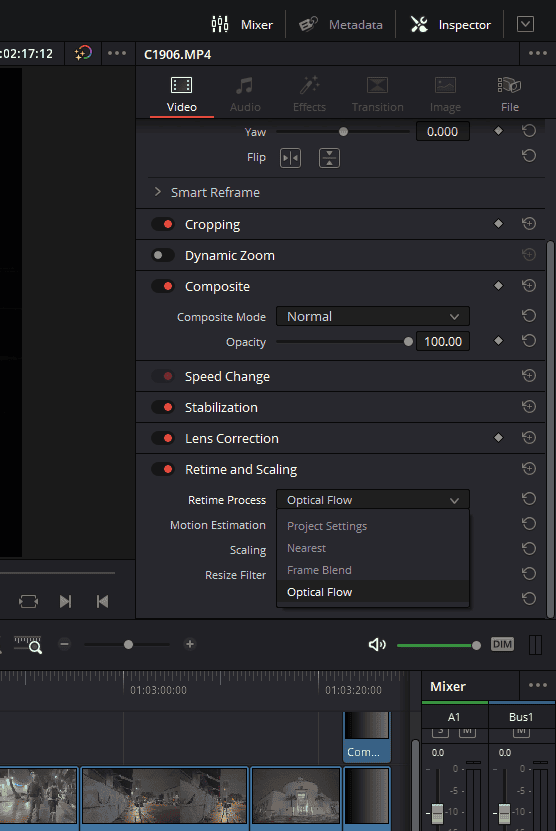
- Locating Retime and Scaling: In the Inspector panel, scroll down until you stumble upon the ‘Retime and Scaling’ section. This section houses the settings for Frame Interpolation techniques including Optical Flow.
Adjusting Retime Process Settings
- Selecting Optical Flow: Within the ‘Retime and Scaling’ section, locate the ‘Retime Process’ drop-down menu. Click on it to expand the menu, and then select ‘Optical Flow’ from the list of options. You can also trade-off between speed and quality by going into the ‘Motion Estimation’ drop-down menu which gives you options to choose how much processing power it should take for Optical Flow to happen. “Enhanced Faster” and “Enhanced Better” are expected to deliver improved outcomes in most scenarios where standard choices display imperfections. However, they require more computational resources, making them slower on many systems.
Reviewing Your Work
- Evaluating the Output: After applying it, play back your clip to observe the smoother motion achieved through this technique. Make any further adjustments if necessary to attain the desired visual fluidity.
Implementing Optical Flow on a Project Level in DaVinci Resolve
The versatility of DaVinci Resolve shines through its capability to apply Optical Flow not only on individual clips but across an entire project. This overarching approach ensures a consistent frame interpolation treatment to all clips necessitating such processing, thereby saving time and promoting uniformity in visual presentation. In this section, we will guide you through a meticulous procedure to activate Optical Flow on the project level.
Setting the Stage for Project Level Optical Flow
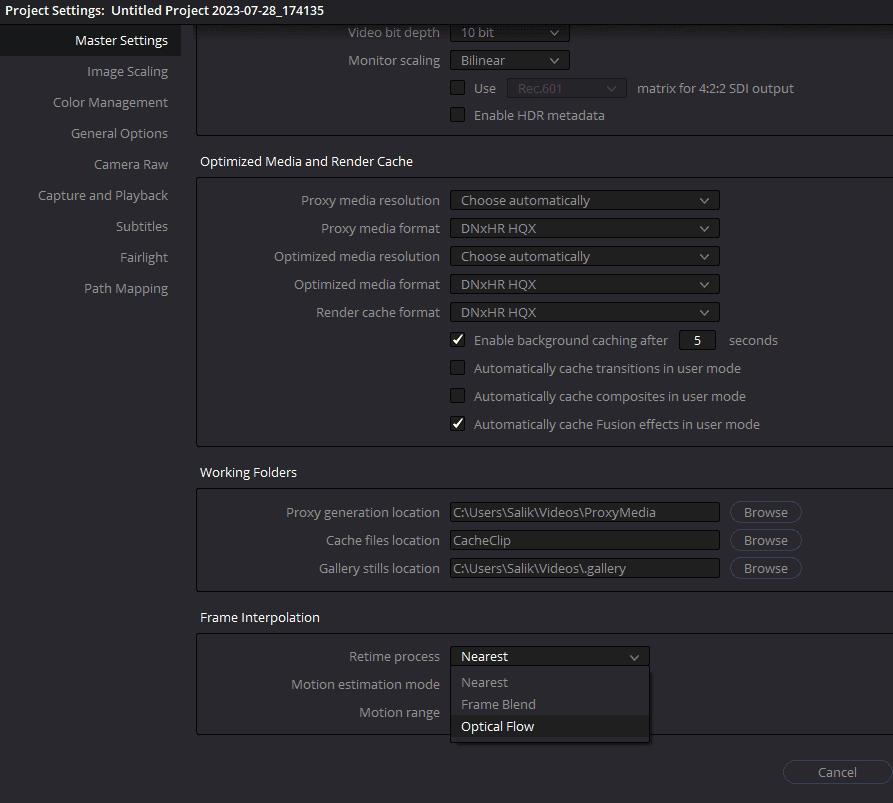
Before embarking on the journey of project-level Optical Flow, it’s prudent to have your project ready and loaded in DaVinci Resolve. Ensure all the clips you intend to work on are properly imported and arranged on the timeline.
Accessing Project Settings
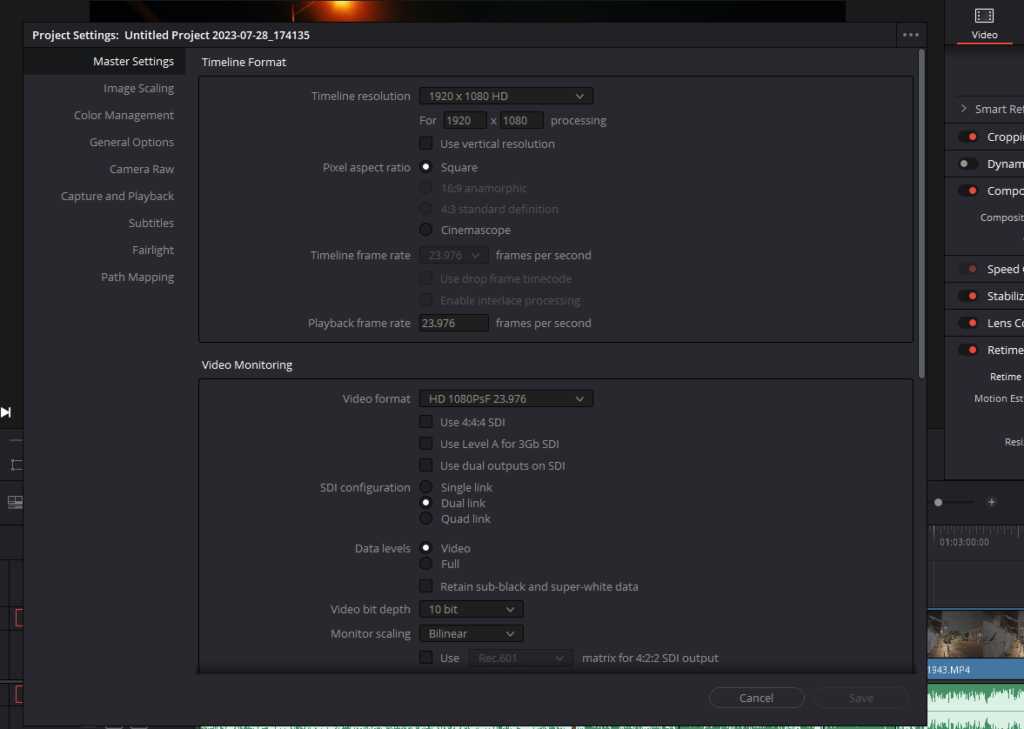
- Navigating to Project Settings: Kickstart the process by clicking on the Project Settings icon, which resembles a gear and is positioned at the bottom right corner of the DaVinci Resolve interface. This action will usher you into the comprehensive project settings realm.
Traversing to Master Settings
- Locating Master Settings: Within the Project Settings dialog, locate and select the ‘Master Settings’ tab. This tab encapsulates a wide array of project-wide configurations, paving the way to the Frame Interpolation section.
Delving into Frame Interpolation Section
- Scrolling to Frame Interpolation: In the Master Settings tab, scroll down the list of options until you unearth the ‘Frame Interpolation’ section. This segment is the gateway to defining how frame interpolation will be handled across your project.
Selecting Optical Flow for Retime Process
- Activating Optical Flow: Within the Frame Interpolation section, spot the ‘Retime Process’ drop-down menu. Click to expand this menu, and amidst the options presented, select ‘Optical Flow’. This action instructs DaVinci Resolve to employ Optical Flow as the default frame interpolation technique for your project.
Applying and Reviewing Your Settings
- Saving Your Configuration: After selecting ‘Optical Flow’, ensure to save your project settings by clicking on the ‘Save’ button. This action will apply Optical Flow across your project, fostering smoother motion in all clips requiring frame interpolation.
- Evaluating the Outcome: Post application, review your timeline and play back the clips to scrutinize the Optical Flow effect.